Page 52 - IDEC relay catalogue
P. 52
Operating Instructions Relays & Sockets
Operating Instructions
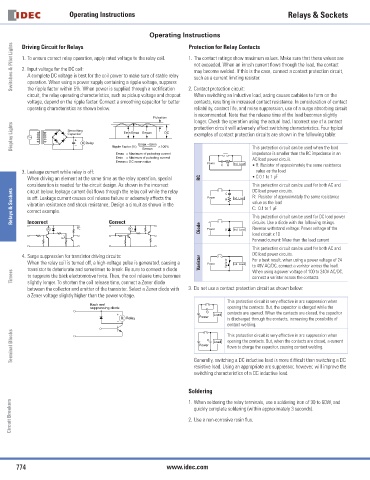
Switches & Pilot Lights 1. To ensure correct relay operation, apply rated voltage to the relay coil. 1. The contact ratings show maximum values. Make sure that these values are
Driving Circuit for Relays
Protection for Relay Contacts
not exceeded. When an inrush current fl ows through the load, the contact
2. Input voltage for the DC coil:
may become welded. If this is the case, connect a contact protection circuit,
A complete DC voltage is best for the coil power to make sure of stable relay
such as a current limiting resistor.
operation. When using a power supply containing a ripple voltage, suppress
the ripple factor within 5%. When power is supplied through a rectifi cation
circuit, the relay operating characteristics, such as pickup voltage and dropout 2. Contact protection circuit:
When switching an inductive load, arcing causes carbides to form on the
voltage, depend on the ripple factor. Connect a smoothing capacitor for better contacts, resulting in increased contact resistance. In consideration of contact
operating characteristics as shown below. reliability, contact life, and noise suppression, use of a surge absorbing circuit
is recommended. Note that the release time of the load becomes slightly
Pulsation
longer. Check the operation using the actual load. Incorrect use of a contact
Display Lights Smoothing R Relay Emin Emax Emean DC examples of contact protection circuits are shown in the following table:
protection circuit will adversely affect switching characteristics. Four typical
Capacitor
+
Emax – Emin
–
× 100%
Ripple Factor (%)
Emean
impedance is smaller than the RC impedance in an
Emax = Maximum of pulsating current This protection circuit can be used when the load
Emin = Minimum of pulsating current AC load power circuit.
Emean= DC mean value
Power Ind. Load
C R • R: Resistor of approximately the same resistance
3. Leakage current while relay is off: value as the load
When driving an element at the same time as the relay operation, special RC • C:0.1 to 1 μF
consideration is needed for the circuit design. As shown in the incorrect C This protection circuit can be used for both AC and
DC load power circuits.
Relays & Sockets is off. Leakage current causes coil release failure or adversely affects the Power R Ind. Load R: Resistor of approximately the same resistance
circuit below, leakage current (Io) fl ows through the relay coil while the relay
value as the load
vibration resistance and shock resistance. Design a circuit as shown in the
C: 0.1 to 1 μF
correct example.
This protection circuit can be used for DC load power
Incorrect
Reverse withstand voltage: Power voltage of the
TE Correct Diode + circuits. Use a diode with the following ratings.
R R Power D Ind. Load
– load circuit x 10
Io
Forward current: More than the load current
This protection circuit can be used for both AC and
4. Surge suppression for transistor driving circuits: DC load power circuits.
When the relay coil is turned off, a high-voltage pulse is generated, causing a Varistor Power Varistor Ind. Load For a best result, when using a power voltage of 24
to 48V AC/DC, connect a varistor across the load.
transistor to deteriorate and sometimes to break. Be sure to connect a diode When using a power voltage of 100 to 240V AC/DC,
Timers to suppress the back electromotive force. Then, the coil release time becomes connect a varistor across the contacts.
slightly longer. To shorten the coil release time, connect a Zener diode
between the collector and emitter of the transistor. Select a Zener diode with 3. Do not use a contact protection circuit as shown below:
a Zener voltage slightly higher than the power voltage.
This protection circuit is very effective in arc suppression when
Back emf
suppressing diode opening the contacts. But, the capacitor is charged while the
C contacts are opened. When the contacts are closed, the capacitor
+ Power Load
R Relay is discharged through the contacts, increasing the possibility of
–
contact welding.
Terminal Blocks Power C Load This protection circuit is very effective in arc suppression when
opening the contacts. But, when the contacts are closed, a current
fl ows to charge the capacitor, causing contact welding.
Generally, switching a DC inductive load is more diffi cult than switching a DC
resistive load. Using an appropriate arc suppressor, however, will improve the
switching characteristics of a DC inductive load.
Soldering
Circuit Breakers 2. Use a non-corrosive rosin fl ux.
1. When soldering the relay terminals, use a soldering iron of 30 to 60W, and
quickly complete soldering (within approximately 3 seconds).
774 www.idec.com