Page 8 - Surge-Protection-E_0.pdf
P. 8
Planned Safety
In addition to the voltage drop at the conventional earthing impedance,
surges are generated in the electrical installation of a building and the i [kA] 100
systems and devices connected to it due to the inductive effect of the 1 2
electromagnetic lightning field (Figure 3, case 3). The energy of these 80 Wave form [µs] 10/350 8/20
20
i max [kA]
100
induced surges and of the resulting impulse currents is far lower than the
energy of a direct lightning impulse current and is therefore described by 60 Prüfstoßstrom für
Test impulse current
a 8/20 μs impulse current wave form (Figure 4). Components and devic- 50 1 Blitzstrom-Ableiter
for lightning current arresters
es that do not have to conduct currents resulting from direct lightning 40
strikes are therefore tested with such 8/20 μs impulse currents.
20 Test impulse current
Protection scheme 2 for surge arresters
Lightning strikes are described as remote if they occur a long distance 0 20 200 350 600 800 1000
from the object to be protected, strike medium-voltage overhead lines or Ref.: EN 61643-11 t [µs]
their surroundings or occur as cloud-to-cloud lightning discharges (Fig-
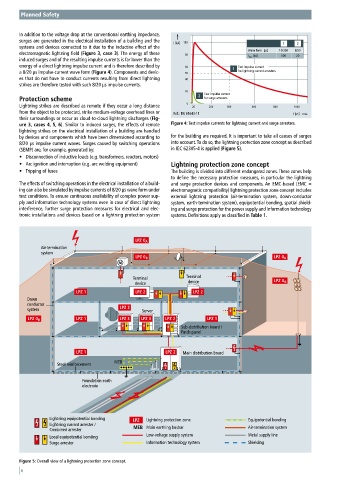
ure 3, cases 4, 5, 6). Similar to induced surges, the effects of remote Figure 4: Test impulse currents for lightning current and surge arresters.
lightning strikes on the electrical installation of a building are handled
by devices and components which have been dimensioned according to for the building are required. It is important to take all causes of surges
8/20 μs impulse current waves. Surges caused by switching operations into account. To do so, the lightning protection zone concept as described
(SEMP) are, for example, generated by: in IEC 62305-4 is applied (Figure 5).
• Disconnection of inductive loads (e.g. transformers, reactors, motors)
• Arc ignition and interruption (e.g. arc welding equipment) Lightning protection zone concept
• Tripping of fuses The building is divided into different endangered zones. These zones help
to define the necessary protection measures, in particular the lightning
The effects of switching operations in the electrical installation of a build- and surge protection devices and components. An EMC-based (EMC =
ing can also be simulated by impulse currents of 8/20 μs wave form under electromagnetic compatibility) lightning protection zone concept includes
test conditions. To ensure continuous availability of complex power sup- external lightning protection (air-termination system, down-conductor
ply and information technology systems even in case of direct lightning system, earth-termination system), equipotential bonding, spatial shield-
interference, further surge protection measures for electrical and elec- ing and surge protection for the power supply and information technology
tronic installations and devices based on a lightning protection system systems. Definitions apply as classified in Table 1.
Air-termination
system
Terminal Terminal
device device
Down
conductor
system Server
Sub-distribution board /
Patch panel
Main distribution board
MEB
Steel reinforcement
Foundation earth
electrode
Lightning equipotential bonding Lightning protection zone Equipotential bonding
Lightning current arrester /
Combined arrester MEB Main earthing busbar Air-termination system
Local equipotential bonding Low-voltage supply system Metal supply line
Surge arrester Information technology system Shielding
Figure 5: Overall view of a lightning protection zone concept.
6