Page 4 - ferraz MV DIN fuse range
P. 4
Mersen Innovations
Striker Mersen HV fuses have
The striker is a mechanical device forming a part of a fuse-link all the striker function
which releases the energy required to cause operation of
another switching device or signalling device. Mersen offers 3 different options to operate
the striker in HV fuses:
The Mersen striker is a “medium” type with an effective
length of 30mm and initial force of 80N. • First one (regular) is driven by the fuse element
when it is melting
The minimum energy is 0.5 Joule.
• Second one (CPD) is driven by the control of the power
dissipation of the fuse-link according to Ohm’s law.
As the back-up fuse-link is combined with a switch the
Controlled Power Dissipation (CPD) operates the switch
before an excessive power level is dissipated by the fuse-link
• Third one is driven by the control of the temperature
of the fuse-link.
Mersen has patented the Thermal Striker (TS)
which monitors the temperature of the fuse-link
and prevents overheating in the fuse compartment
when installed with a switch-fuse combination.
The two latter options are additional functions
available in some ranges.
Melting curves
With CPD and TS, the fuse-link will not switch-off by itself.
The purpose of these both functions is to trigger the switch in
combination to switch off.
Thermal Striker description
• As demanded by switch-fuse combination manufacturers,
the thermal stricker has to trigger the switch to open the three
phases in case of abnormal condition like overheating.
• The purpose of this invention is to propose a fuse that
is designed for switch-fuse combinations and capable
of opening the circuit when an extended over-current causes
temperature to rise. Our new patented thermal striker fulfi ls
this function: whenever the temperature rises abnormally
in a fuse, the thermal striker trips and triggers either
a mechanical or an electronic system that will open the circuit
(sketch).
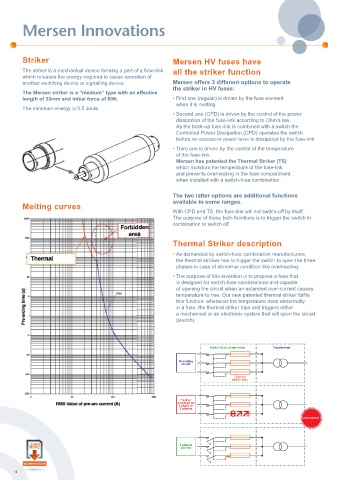
Switch-fuse combination Transformer
Operating
circuit
Thermal
striker-fuse
Fault or
overload on
1 phase or
2 phases
overcurrent
3 phases
opened
4