Page 12 - V16 Catalogue Final
P. 12
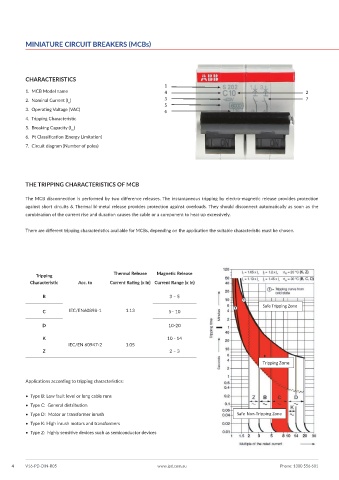
MINIATURE CIRCUIT BREAKERS (MCBs)
CHARACTERISTICS
1
1. MCB Model name 4 2
2. Nominal Current (I ) 3 7
n
5
3. Operating Voltage (VAC) 6
4. Tripping Characteristic
5. Breaking Capacity (I )
cn
6. I t Classification (Energy Limitation)
2
7. Circuit diagram (Number of poles)
THE TRIPPING CHARACTERISTICS OF MCB
The MCB disconnection is performed by two difference releases. The instantaneous tripping by electro-magnetic release provides protection
against short circuits & Thermal bi-metal release provides protection against overloads. They should disconnect automatically as soon as the
combination of the current rise and duration causes the cable or a component to heat up excessively.
There are different tripping characteristics available for MCBs, depending on the application the suitable characteristic must be chosen.
Tripping Thermal Release Magnetic Release
Characteristic Acc. to Current Rating (x In) Current Range (x In)
B 3 – 5
Safe Tripping Zone
C IEC/EN60898-1 1.13 5– 10
D 10-20
K 10 - 14
IEC/EN 60947-2 1.05
Z 2 – 3
Tripping Zone
Applications according to tripping characteristics:
• Type B: Low fault level or long cable runs
• Type C: General distribution
• Type D: Motor or transformer inrush Safe Non-Tripping Zone
• Type K: High inrush motors and transformers
• Type Z: highly sensitive devices such as semiconductor devices
4 V16-PD-DIN-R05 www.ipd.com.au Phone: 1300 556 601