Page 13 - V16 Catalogue Final
P. 13
RESIDUAL CURRENT DEVICE (RCD)
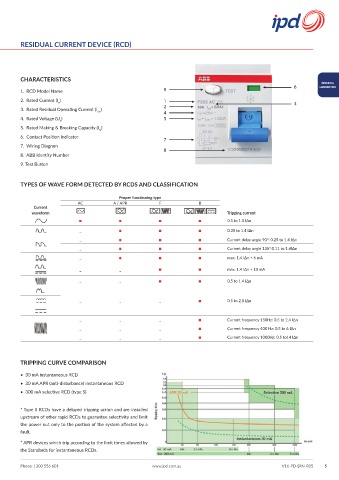
CHARACTERISTICS
DIN MCB &
6 LOADCENTRES
1. RCD Model Name 9
2. Rated Current (I ) 1 3
n
3. Rated Residual Operating Current (I ) 2 4
Δn
4. Rated Voltage (U ) 5
n
5. Rated Making & Breaking Capacity (I )
m
6. Contact Position Indicator
7
7. Wiring Diagram
8
8. ABB Identity Number
9. Test Button
TYPES OF WAVE FORM DETECTED BY RCDS AND CLASSIFICATION
Proper functioning type
AC A / APR F B
Current
waveform Tripping current
▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ 0.5 to 1.0 IΔn
_ ▪ ▪ ▪ 0.35 to 1.4 IΔn
_ ▪ ▪ ▪ Current delay angle 90°: 0.25 to 1.4 IΔn
_ ▪ ▪ ▪ Current delay angle 135°:0.11 to 1.4IΔn
▪ ▪ ▪
_ max. 1.4 IΔn + 6 mA
_ _ ▪ ▪ max. 1.4 IΔn + 10 mA
_ _ ▪ ▪ 0.5 to 1.4 IΔn
_ _ _ ▪ 0.5 to 2.0 IΔn
▪
_ _ _ Current frequency 150Hz: 0.5 to 2.4 IΔn
_ _ _ ▪ Current frequency 400 Hz: 0.5 to 6 IΔn
_ _ _ ▪ Current frequency 1000Hz: 0.5 to14 IΔn
TRIPPING CURVE COMPARISON
• 30 mA instantaneous RCD
• 30 mA APR (anti-disturbance) instantaneous RCD
• 300 mA selective RCD (type S)
* Type S RCDs have a delayed tripping action and are installed
upstream of other rapid RCDs to guarantee selectivity and limit
the power out only to the portion of the system affected by a
fault.
* APR devices which trip according to the limit times allowed by
the Standards for instantaneous RCDs.
Phone: 1300 556 601 www.ipd.com.au V16-PD-DIN-R05 5