Page 14 - Product catalogue v17
P. 14
Circuit Breakers & Load Centres
MINIATURE CIRCUIT BREAKERS (MCB)
Characteristics
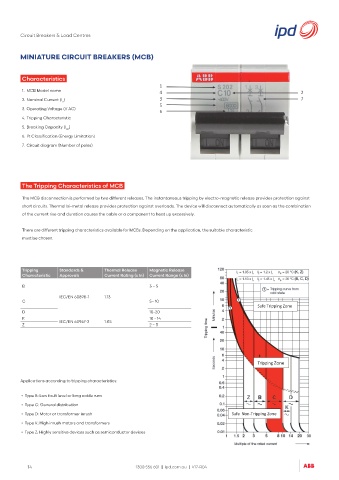
1. MCB Model name
2. Nominal Current (I )
n
3. Operating Voltage (V AC)
4. Tripping Characteristic
5. Breaking Capacity (I )
cn
6. I t Classification (Energy Limitation)
2
7. Circuit diagram (Number of poles)
The Tripping Characteristics of MCB
The MCB disconnection is performed by two different releases. The instantaneous tripping by electro-magnetic release provides protection against
short circuits. Thermal bi-metal release provides protection against overloads. The device will disconnect automatically as soon as the combination
of the current rise and duration causes the cable or a component to heat up excessively.
There are different tripping characteristics available for MCBs. Depending on the application, the suitable characteristic
must be chosen.
Tripping Standards & Thermal Release Magnetic Release
Characteristic Approvals Current Rating (x In) Current Range (x In)
B 3 – 5
IEC/EN 60898-1 1.13
C 5– 10
Safe Tripping Zone
D 10-20
K IEC/EN 60947-2 1.05 10 - 14
Z 2 – 3
Tripping Zone
Applications according to tripping characteristics:
• Type B: Low fault level or long cable runs
• Type C: General distribution
• Type D: Motor or transformer inrush Safe Non-Tripping Zone
• Type K: High inrush motors and transformers
• Type Z: Highly sensitive devices such as semiconductor devices
14 1300 556 601 | ipd.com.au | V17-R08