Page 10 - Fuse link Catalogue
P. 10
CIRCUIT LOADING
Circuit Loading
The HRC fuse link selected for any circuit should have a continuous current rating not less than the full
load current of the circuit.
Complete Cable Protection
A standard rating of type ‘T’ fuse link (classified as type ‘gG’ to BS88:Part 1:1988, and marked
accordingly) will protect an associated pvc insulated cable against both overload and short circuit if its
current rating (In) is equal to, or less than the current rating of the cable (I2). This is in accordance with
rule 2.4.2.1. listed in AS3000-1991.
Short Circuit Energy Limitation
Type ‘T’ fuse links limit the peak current and energy Protection of Cables against Short Circuit Faults
let-through to circuit which experience major short In some circuits (eg, motor circuits) it is not economical practice to match fuse link and
circuit faults. This limitation is so great that equipment cable ratings to provide complete cable protection in the manner described above,
manufacturers exploit it to product economic designs because the circuits produce significant over currents during transient conditions. In such
which, when used in combination with type ‘T’ fuse cases the fuse links are chosen to withstand the transient conditions, and provide only
links, can withstand very high fault levels. Such users short circuit protection to the associated cables and other circuit components, the
have to prove their equipment under the worst possible necessary overload protection then being provided by other means. In a motor circuit, for
conditions (ie. at maximum breaking capacity, at 110% example the contactor and its overload relays afford overload protection to motor
rated voltage, very low power factor , and with faults windings and cable and the fuse links are chosen to protect all the circuit components
initiated at most onerous points on the voltage wave), against damage when a short circuit fault occurs (see section on motor circuit protection
and they require relevant data from the fuse link on page 10). The short circuit protection of cables is covered by Section 5 of
manufacturer. For type ‘T’ fuse links this is given in the AS3008.1-1989 and the table shows how Type T fuse links relate to this rule in
2
form of the cut-off current and I t characteristics shown protecting pvc insulated copper conductors.
on pages 12 to 17 inclusive.
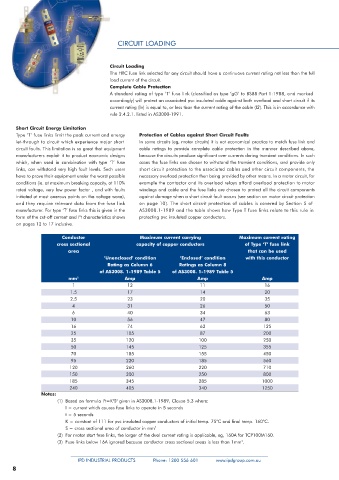
Conductor Maximum current carrying Maximum current rating
cross sectional capacity of copper conductors of Type ‘T’ fuse link
area that can be used
‘Unenclosed’ condition ‘Enclosed’ condition with this conductor
Rating as Column 6 Ratings as Column 8
of AS3008. 1-1989 Table 5 of AS3008. 1-1989 Table 5
mm 2 Amp Amp Amp
1 13 11 16
1.5 17 14 20
2.5 23 20 35
4 31 26 50
6 40 34 63
10 56 47 80
16 74 62 125
25 105 87 200
35 120 100 250
50 145 125 355
70 185 155 450
95 220 185 560
120 260 220 710
150 300 250 800
185 345 285 1000
240 405 340 1250
Notes:
(1) Based on formula I t=K S given in AS3008.1-1989, Clause 5.3 where:
2
2
2
I = current which causes fuse links to operate in 5 seconds
t = 5 seconds
K = constant of 111 for pvc insulated copper conductors of initial temp. 75°C and final temp. 160°C.
S = cross sectional area of conductor in mm 2
(2) For motor start fuse links, the larger of the dual current rating is applicable, eg, 160A for TCP100M160.
2
(3) Fuse links below 16A ignored because conductor cross sectional areas is less than 1mm .
IPD INDUSTRIAL PRODUCTS Phone: 1300 556 601 www.ipdgroup.com.au
8