Page 18 - B_ELSB_Cat_2022_01_MCBs
P. 18
1/18 ELECTRICAL INSTALL ATION SOLUTIONS FOR BUILDINGS - TECHNICAL DETAILS 9AKK 107991 A8329
1
—
MCBs technical details
2
Limitation of specific let-through energy I t
Limitation of specific let-through energy This can be achieved using mechanisms which open very
Tripping of an installation circuit by circuit-breaker when rapidly and have the following advantages:
there is a short-circuit requires a certain amount of time • they limit the thermal and dynamic effects both on
depending on the characteristics of the circuit-breaker the circuit-breaker and on the protected circuit;
and the entity of the short-circuit current. During this • they reduce the dimensions of the current-limiting
period of time, some or all of the short-circuit current flows circuit-breaker without reducing breaking capacity;
2
into the installation; the parameter I t defines the “specific • they considerably reduce ionized gases and sparklers
let-through energy”, ie. the specific energy that the breaker emitted during the short-circuit and therefore they avoid
allows through when there is a short-circuit current Icc the danger of ignition and fires.
during the tripping time t.
In this way, we can determine the capacity
of a circuit-breaker to limit, ie. break high currents up
to the rated breaking power of the device, by reducing
the peak value of the above-mentioned currents to a value
which is considerably lower than the estimated current.
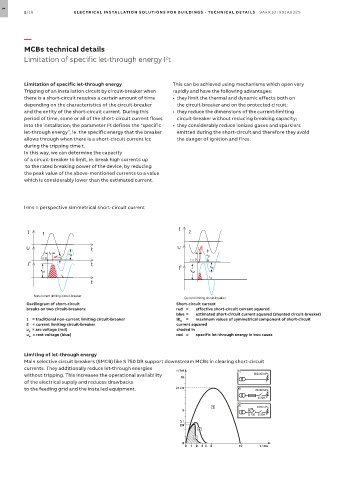
Irms = perspective simmetrical short-circuit current
I I
I 1 I 1 2 2
U
U t U t v U t v
t v u u B t u
t = 0 u B M t = 0 t v t = 0 u M t = 0 B
u
I 2 t I 2 I 2 B u M t I 2 u
K M i K M i K M M
K M
i K i K i K i K
t t
Non-current limiting circuit-breaker Current limiting circuit-breaker
Non-current limiting circuit-breaker Current limiting circuit-breaker
Oscillogram of short-circuit Short-circuit current
breaks on two circuit-breakers: red = effective short-circuit current squared
blue = estimated short-circuit current squared (shunted circuit-breaker)
1 = traditional non-current limiting circuit-breaker iK = maximum values of symmetrical component of short-circuit
M
2 = current limiting circuit-breaker current squared
u = arc voltage (red) shaded in
B
u = rest voltage (blue) red = specific let-through energy in two cases
M
Limiting of let-through energy
Main selective circuit breakers (SMCB) like S 750 DR support downstream MCBs in clearing short-circuit
currents. They additionally reduce let-through energies
without tripping. This increases the operational availability
of the electrical supply and reduces drawbacks
to the feeding grid and the installed equipment.