Page 19 - B_ELSB_Cat_2022_01_MCBs
P. 19
1
1/19
—
MCBs technical details
2
Limitation of specific let-through energy I t
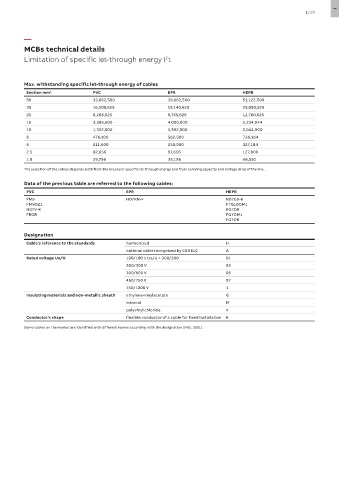
Max. withstanding specific let-through energy of cables
Section mm 2 PVC EPR HEPR
50 33,062,500 39,062,500 51,122,500
35 16,200,625 19,140,625 25,050,025
25 8,265,625 9,765,625 12,780,625
16 3,385,600 4,000,000 5,234,944
10 1,322,500 1,562,500 2,044,900
6 476,100 562,500 736,164
4 211,600 250,000 327,184
2.5 82,656 97,656 127,806
1.5 29,756 35,156 46,010
The selection of the cables depends both from the breakers’ specific let-through energy and from carrying capacity and voltage drop of the line.
Data of the previous table are referred to the following cables:
PVC EPR HEPR
FM9 H07RN-F N07G9-K
FM9OZ1 FTG10OM1
N07V-K RG7OR
FROR FG7OM1
FG7OR
Designation
Cable’s reference to the standards harmonized H
national cable recognized by CENELC A
Rated voltage Uo/U 100/100 ≤ Uo/U < 300/300 01
300/300 V 03
300/500 V 05
450/750 V 07
750/1000 V 1
Insulating materials and non-metallic sheath ethylene-vinylacetate G
mineral M
polyvinyl chloride V
Conductor’s shape flexible conductor of a cable for fixed installation K
Some cables on the market are identified with different names according with the designation UNEL 35011.