Page 212 - 35_DS702_E_2014_Lightning_Protection_Guide
P. 212
Spark gap bined arresters). In this process, coordination with a reference
¨ After an extremely short period of time, the voltage drops varistor of type S20K275 was tested, which is a typical protec-
to the so-called arc voltage which in case of a modern fol- tive circuit in a terminal device in case of a supply voltage of
low current limiting spark gap is typically in the range of 230 V.
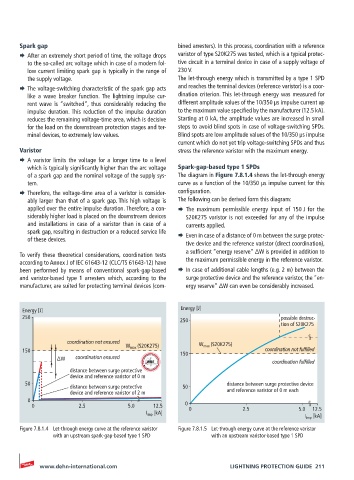
the supply voltage. The let-through energy which is transmitted by a type 1 SPD
¨ The voltage-switching characteristic of the spark gap acts and reaches the terminal devices (reference varistor) is a coor-
like a wave breaker function. The lightning impulse cur- dination criterion. This let-through energy was measured for
rent wave is “switched”, thus considerably reducing the different amplitude values of the 10/350 µs impulse current up
impulse duration. This reduction of the impulse duration to the maximum value specified by the manufacturer (12.5 kA).
reduces the remaining voltage-time area, which is decisive Starting at 0 kA, the amplitude values are increased in small
for the load on the downstream protection stages and ter- steps to avoid blind spots in case of voltage-switching SPDs.
minal devices, to extremely low values. Blind spots are low amplitude values of the 10/350 µs impulse
current which do not yet trip voltage-switching SPDs and thus
Varistor stress the reference varistor with the maximum energy.
¨ A varistor limits the voltage for a longer time to a level
which is typically significantly higher than the arc voltage Spark-gap-based type 1 SPDs
of a spark gap and the nominal voltage of the supply sys- The diagram in Figure 7.8.1.4 shows the let-through energy
tem. curve as a function of the 10/350 µs impulse current for this
¨ Therefore, the voltage-time area of a varistor is consider- configuration.
ably larger than that of a spark gap. This high voltage is The following can be derived form this diagram:
applied over the entire impulse duration. Therefore, a con- ¨ The maximum permissible energy input of 150 J for the
siderably higher load is placed on the downstream devices S20K275 varistor is not exceeded for any of the impulse
and installations in case of a varistor than in case of a currents applied.
spark gap, resulting in destruction or a reduced service life
of these devices. ¨ Even in case of a distance of 0 m between the surge protec-
tive device and the reference varistor (direct coordination),
a sufficient “energy reserve” ∆W is provided in addition to
To verify these theoretical considerations, coordination tests
according to Annex J of IEC 61643-12 (CLC/TS 61643-12) have the maximum permissible energy in the reference varistor.
been performed by means of conventional spark-gap-based ¨ In case of additional cable lengths (e.g. 2 m) between the
and varistor-based type 1 arresters which, according to the surge protective device and the reference varistor, the “en-
manufacturer, are suited for protecting terminal devices (com- ergy reserve” ∆W can even be considerably increased.
Energy [J] Energy [J]
250 possible destruc-
250
tion of S20K275
coordination not ensured W max (S20K275) W max (S20K275)
150 150 coordination not fulfilled
∆W coordination ensured
coordination fulfilled
distance between surge protective
device and reference varistor of 0 m
50 distance between surge protective device
distance between surge protective 50
device and reference varistor of 2 m and reference varistor of 0 m each
0
0 2.5 5.0 12.5 0 0 2.5 5.0 12.5
I imp [kA]
I imp [kA]
Figure 7.8.1.4 Let-through energy curve at the reference varistor Figure 7.8.1.5 Let-through energy curve at the reference varistor
with an upstream spark-gap-based type 1 SPD with an upstream varistor-based type 1 SPD
www.dehn-international.com LIGHTNING PROTECTION GUIDE 211