Page 438 - 35_DS702_E_2014_Lightning_Protection_Guide
P. 438
During producing, processing, storing and transporting flam- According to the lightning protection zone concept as per
mable substances (e.g. fuel, alcohol, liquid gas, explosive IEC 62305-4 (EN 62305-4), adequate surge protective devices,
dusts), potentially explosive atmospheres where no ignition which will be described below, must be provided for all lines at
sources may be present to prevent explosion frequently occur the boundaries of the lightning protection zones.
in chemical and petrochemical industrial plants. The relevant
safety regulations describe the risk for such plants posed by at- External lightning protection system
mospheric discharges (lightning strikes). In this context, it must The external lightning protection system includes all systems
be observed that there is a risk of fire and explosion resulting installed outside or inside the structure to be protected for in-
from direct or indirect lightning discharge since in some cases tercepting and discharging the lightning current to the earth-
these plants are widely distributed. termination system.
To ensure the required plant availability and safety, a concep- A lightning protection system for potentially explosive atmos-
tual procedure is required to protect parts of electrical and pheres is typically designed according to class of LPS II. An-
electronic installations of process plants from lightning cur- other class of LPS can be chosen in justified individual cases,
rents and surges. in case of special conditions (legal requirements) or as a result
of a risk analysis. The requirements described below are based
Protection concept on class of LPS II.
Intrinsically safe measuring circuits are frequently used in
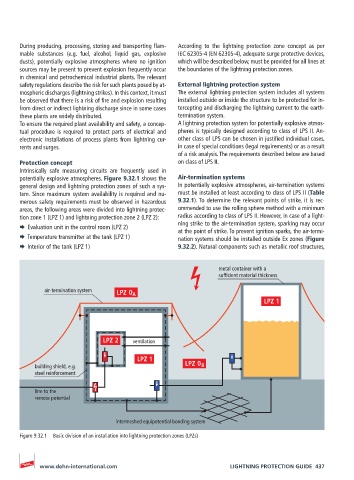
potentially explosive atmospheres. Figure 9.32.1 shows the Air-termination systems
general design and lightning protection zones of such a sys- In potentially explosive atmospheres, air-termination systems
tem. Since maximum system availability is required and nu- must be installed at least according to class of LPS II (Table
merous safety requirements must be observed in hazardous 9.32.1). To determine the relevant points of strike, it is rec-
areas, the following areas were divided into lightning protec- ommended to use the rolling sphere method with a minimum
tion zone 1 (LPZ 1) and lightning protection zone 2 (LPZ 2): radius according to class of LPS II. However, in case of a light-
ning strike to the air-termination system, sparking may occur
¨ Evaluation unit in the control room (LPZ 2)
at the point of strike. To prevent ignition sparks, the air-termi-
¨ Temperature transmitter at the tank (LPZ 1) nation systems should be installed outside Ex zones (Figure
¨ Interior of the tank (LPZ 1) 9.32.2). Natural components such as metallic roof structures,
metal container with a
sufficient material thickness
air-termination system
ventilation
building shield, e.g.
steel reinforcement
line to the
remote potential
intermeshed equipotential bonding system
Figure 9.32.1 Basic division of an installation into lightning protection zones (LPZs)
www.dehn-international.com LIGHTNING PROTECTION GUIDE 437