Page 356 - 35_DS702_E_2014_Lightning_Protection_Guide
P. 356
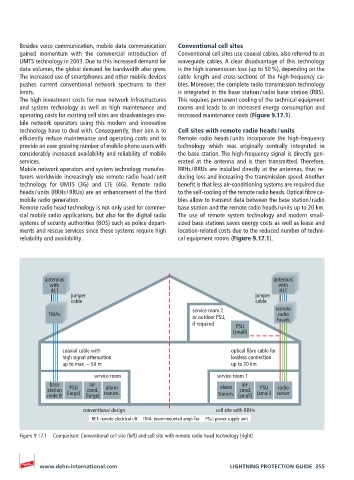
Besides voice communication, mobile data communication Conventional cell sites
gained momentum with the commercial introduction of Conventional cell sites use coaxial cables, also referred to as
UMTS technology in 2003. Due to this increased demand for waveguide cables. A clear disadvantage of this technology
data volumes, the global demand for bandwidth also grew. is the high transmission loss (up to 50 %), depending on the
The increased use of smartphones and other mobile devices cable length and cross-sections of the high-frequency ca-
pushes current conventional network spectrums to their bles. More over, the complete radio transmission technology
limits. is integrated in the base station / radio base station (RBS).
The high investment costs for new network infrastructures This requires permanent cooling of the technical equipment
and system technology as well as high maintenance and rooms and leads to an increased energy consumption and
operating costs for existing cell sites are disadvantages mo- increased maintenance costs (Figure 9.17.1).
bile network operators using this modern and innovative
technology have to deal with. Consequently, their aim is to Cell sites with remote radio heads / units
efficiently reduce maintenance and operating costs and to Remote radio heads / units incorporate the high-frequency
provide an ever growing number of mobile phone users with technology which was originally centrally integrated in
considerably increased availability and reliability of mobile the base station. The high-frequency signal is directly gen-
services. erated at the antenna and is then transmitted. Therefore,
Mobile network operators and system technology manufac- RRHs / RRUs are installed directly at the antennas, thus re-
turers worldwide increasingly use remote radio head / unit ducing loss and increasing the transmission speed. Another
technology for UMTS (3G) and LTE (4G). Remote radio benefit is that less air-conditioning systems are required due
heads / units (RRHs / RRUs) are an enhancement of the third to the self-cooling of the remote radio heads. Optical fibre ca-
mobile radio generation. bles allow to transmit data between the base station / radio
Remote radio head technology is not only used for commer- base station and the remote radio heads / units up to 20 km.
cial mobile radio applications, but also for the digital radio The use of remote system technology and modern small-
systems of security authorities (BOS) such as police depart- sized base stations saves energy costs as well as lease and
ments and rescue services since these systems require high location-related costs due to the reduced number of techni-
reliability and availability. cal equipment rooms (Figure 9.17.1).
antennas antennas
with with
RET RET
jumper jumper
cable cable
service room 2 remote
TMAs radio
or outdoor PSU, heads
if required PSU
(small)
coaxial cable with optical fibre cable for
high signal attenuation lossless connection
up to max. ~ 50 m up to 20 km
service room service room 1
base air- air-
station PSU cond. alarm alarm cond. PSU radio
node B (large) (large) transm. transm. (small) (small) server
conventional design cell site with RRHs
RET: remote electrical tilt TMA: tower-mounted amplifier PSU: power supply unit
Figure 9.17.1 Comparison: Conventional cell site (left) and cell site with remote radio head technology (right)
www.dehn-international.com LIGHTNING PROTECTION GUIDE 355