Page 146 - 35_DS702_E_2014_Lightning_Protection_Guide
P. 146
i
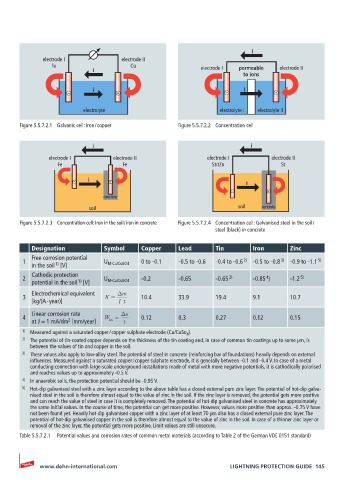
electrode I electrode II
Fe Cu electrode I permeable electrode II
i
to ions
i i
electrolyte electrolyte I electrolyte II
Figure 5.5.7.2.1 Galvanic cell: Iron / copper Figure 5.5.7.2.2 Concentration cell
i i
electrode I electrode II electrode I electrode II
Fe Fe St/tZn St
i
i
concrete
soil soil concrete
Figure 5.5.7.2.3 Concentration cell: Iron in the soil / iron in concrete Figure 5.5.7.2.4 Concentration cell: Galvanised steel in the soil /
steel (black) in concrete
Designation Symbol Copper Lead Tin Iron Zinc
Free corrosion potential
1 U M-Cu/CuSO4 0 to –0.1 –0.5 to –0.6 –0.4 to –0.6 2) –0.5 to –0.8 3) –0.9 to –1.1 5)
1)
in the soil [V]
Cathodic protection
2 U M-Cu/CuSO4 –0.2 –0.65 –0.65 2) –0.85 ) –1.2 5)
4
potential in the soil [V]
1)
Electrochemical equivalent m
3 K = 10.4 33.9 19.4 9.1 10.7
[kg/(A · year)] I t
Linear corrosion rate s
4 W = 0.12 0.3 0.27 0.12 0.15
2
at J = 1 mA/dm [mm/year] lin t
1) Measured against a saturated copper / copper sulphate electrode (Cu/CuSo ).
4
2) The potential of tin-coated copper depends on the thickness of the tin coating and, in case of common tin coatings up to some μm, is
between the values of tin and copper in the soil.
3) These values also apply to low-alloy steel. The potential of steel in concrete (reinforcing bar of foundations) heavily depends on external
influences. Measured against a saturated copper / copper sulphate electrode, it is generally between –0.1 and –0.4 V. In case of a metal
conducting connection with large-scale underground installations made of metal with more negative potentials, it is cathodically polarised
and reaches values up to approximately –0.5 V.
4) In anaerobic soils, the protection potential should be –0.95 V.
5) Hot-dip galvanised steel with a zinc layer according to the above table has a closed external pure zinc layer. The potential of hot-dip galva-
nised steel in the soil is therefore almost equal to the value of zinc in the soil. If the zinc layer is removed, the potential gets more positive
and can reach the value of steel in case it is completely removed. The potential of hot-dip galvanised steel in concrete has approximately
the same initial values. In the course of time, the potential can get more positive. However, values more positive than approx. –0.75 V have
not been found yet. Heavily hot-dip galvanised copper with a zinc layer of at least 70 μm also has a closed external pure zinc layer. The
potential of hot-dip galvanised copper in the soil is therefore almost equal to the value of zinc in the soil. In case of a thinner zinc layer or
removal of the zinc layer, the potential gets more positive. Limit values are still unsecure.
Table 5.5.7.2.1 Potential values and corrosion rates of common metal materials (according to Table 2 of the German VDE 0151 standard)
www.dehn-international.com LIGHTNING PROTECTION GUIDE 145