Page 150 - 35_DS702_E_2014_Lightning_Protection_Guide
P. 150
5.5.7.5 Other anti-corrosion measures trical installations in the structure requiring protection is not
Connecting cables / terminal lugs between founda- sufficient.
tion earth electrodes and down conductors Metal installations such as water, air-conditioning and elec-
Galvanised steel connecting cables between foundation earth tric lines form induction loops in the building where impulse
electrodes and down conductors should be laid in concrete or voltages are induced due to the quickly changing magnetic
lightning field. It must be prevented that these impulse volt-
masonry until they are above the surface of the earth. ages cause uncontrolled flashover which can also result in fire.
If the connecting cables are led through the ground, terminal Flashover on electric lines, for example, can cause enormous
2
lugs with e.g. NYY cable, 1 x 16 mm Cu, stainless steel (V4A), damage to the installation and the connected loads. Figure
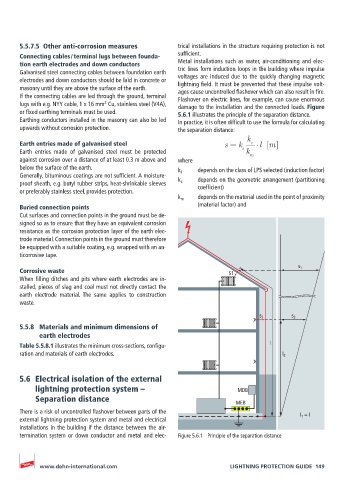
or fixed earthing terminals must be used. 5.6.1 illustrates the principle of the separation distance.
Earthing conductors installed in the masonry can also be led In practice, it is often difficult to use the formula for calculating
upwards without corrosion protection. the separation distance:
k
Earth entries made of galvanised steel s = k c l [m]
Earth entries made of galvanised steel must be protected i k m
against corrosion over a distance of at least 0.3 m above and where
below the surface of the earth. k i depends on the class of LPS selected (induction factor)
Generally, bituminous coatings are not sufficient. A moisture- k c depends on the geometric arrangement (partitioning
proof sheath, e.g. butyl rubber strips, heat-shrinkable sleeves coefficient)
or preferably stainless steel, provides protection.
k m depends on the material used in the point of proximity
Buried connection points (material factor) and
Cut surfaces and connection points in the ground must be de-
signed so as to ensure that they have an equivalent corrosion
resistance as the corrosion protection layer of the earth elec-
trode material. Connection points in the ground must therefore
be equipped with a suitable coating, e.g. wrapped with an an-
ticorrosive tape.
s 1
Corrosive waste S1
When filling ditches and pits where earth electrodes are in-
stalled, pieces of slag and coal must not directly contact the
earth electrode material. The same applies to construction
waste.
s 2 s 2
5.5.8 Materials and minimum dimensions of
earth electrodes
Table 5.5.8.1 illustrates the minimum cross-sections, configu- l
ration and materials of earth electrodes. l 2
5.6 Electrical isolation of the external
lightning protection system – MDB
Separation distance MEB
There is a risk of uncontrolled flashover between parts of the l 1 = l
external lightning protection system and metal and electrical
installations in the building if the distance between the air-
termination system or down conductor and metal and elec- Figure 5.6.1 Principle of the separation distance
www.dehn-international.com LIGHTNING PROTECTION GUIDE 149