Page 41 - 35_DS702_E_2014_Lightning_Protection_Guide
P. 41
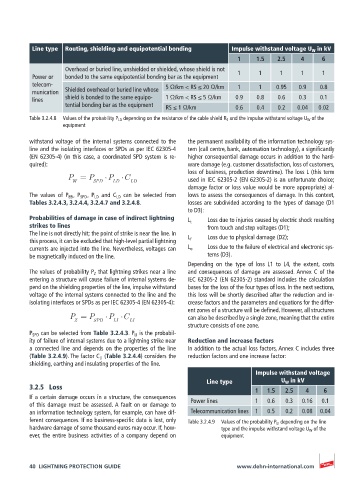
Line type Routing, shielding and equipotential bonding Impulse withstand voltage U W in kV
1 1.5 2.5 4 6
Overhead or buried line, unshielded or shielded, whose shield is not
Power or bonded to the same equipotential bonding bar as the equipment 1 1 1 1 1
telecom- 5 Ω/km < RS ≤ 20 Ω/km 1 1 0.95 0.9 0.8
munication Shielded overhead or buried line whose
lines shield is bonded to the same equipo- 1 Ω/km < RS ≤ 5 Ω/km 0.9 0.8 0.6 0.3 0.1
tential bonding bar as the equipment RS ≤ 1 Ω/km 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.04 0.02
Table 3.2.4.8 Values of the probability P LD depending on the resistance of the cable shield R S and the impulse withstand voltage U W of the
equipment
withstand voltage of the internal systems connected to the the permanent availability of the information technology sys-
line and the isolating interfaces or SPDs as per IEC 62305-4 tem (call centre, bank, automation technology), a significantly
(EN 62305-4) (in this case, a coordinated SPD system is re- higher consequential damage occurs in addition to the hard-
quired): ware damage (e.g. customer dissatisfaction, loss of customers,
loss of business, production downtime). The loss L (this term
P = P P C used in IEC 62305-2 (EN 62305-2) is an unfortunate choice;
W SPD LD LD
damage factor or loss value would be more appropriate) al-
The values of P EB , P SPD , P LD and C LD can be selected from lows to assess the consequences of damage. In this context,
Tables 3.2.4.3, 3.2.4.4, 3.2.4.7 and 3.2.4.8. losses are subdivided according to the types of damage (D1
to D3):
Probabilities of damage in case of indirect lightning L t Loss due to injuries caused by electric shock resulting
strikes to lines from touch and step voltages (D1);
The line is not directly hit; the point of strike is near the line. In L f Loss due to physical damage (D2);
this process, it can be excluded that high-level partial lightning
currents are injected into the line. Nevertheless, voltages can L o Loss due to the failure of electrical and electronic sys-
be magnetically induced on the line. tems (D3).
Depending on the type of loss L1 to L4, the extent, costs
The values of probability P Z that lightning strikes near a line and consequences of damage are assessed. Annex C of the
entering a structure will cause failure of internal systems de- IEC 62305-2 (EN 62305-2) standard includes the calculation
pend on the shielding properties of the line, impulse withstand bases for the loss of the four types of loss. In the next sections,
voltage of the internal systems connected to the line and the this loss will be shortly described after the reduction and in-
isolating interfaces or SPDs as per IEC 62305-4 (EN 62305-4): crease factors and the parameters and equations for the differ-
ent zones of a structure will be defined. However, all structures
P = P P C can also be described by a single zone, meaning that the entire
Z SPD LI LI
structure consists of one zone.
P SPD can be selected from Table 3.2.4.3. P LI is the probabil-
ity of failure of internal systems due to a lightning strike near Reduction and increase factors
a connected line and depends on the properties of the line In addition to the actual loss factors, Annex C includes three
(Table 3.2.4.9). The factor C LI (Table 3.2.4.4) considers the reduction factors and one increase factor:
shielding, earthing and insulating properties of the line.
Impulse withstand voltage
Line type U W in kV
3.2.5 Loss
1 1.5 2.5 4 6
If a certain damage occurs in a structure, the consequences Power lines 1 0.6 0.3 0.16 0.1
of this damage must be assessed. A fault on or damage to
an information technology system, for example, can have dif- Telecommunication lines 1 0.5 0.2 0.08 0.04
ferent consequences. If no business-specific data is lost, only Table 3.2.4.9 Values of the probability P LI depending on the line
hardware damage of some thousand euros may occur. If, how- type and the impulse withstand voltage U W of the
ever, the entire business activities of a company depend on equipment
40 LIGHTNING PROTECTION GUIDE www.dehn-international.com