Page 42 - 35_DS702_E_2014_Lightning_Protection_Guide
P. 42
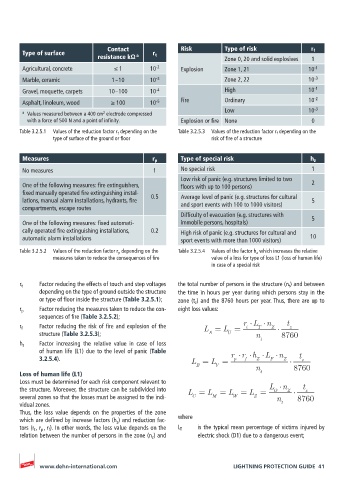
Contact Risk Type of risk r f
Type of surface r t
resistance kΩ a Zone 0, 20 and solid explosives 1
Agricultural, concrete ≤ 1 10 -2 Explosion Zone 1, 21 10 -1
Marble, ceramic 1 – 10 10 -3 Zone 2, 22 10 -3
Gravel, moquette, carpets 10 – 100 10 -4 High 10 -1
Asphalt, linoleum, wood ≥ 100 10 -5 Fire Ordinary 10 -2
Low 10 -3
2
a Values measured between a 400 cm electrode compressed
with a force of 500 N and a point of infinity. Explosion or fire None 0
Table 3.2.5.1 Values of the reduction factor r t depending on the Table 3.2.5.3 Values of the reduction factor r f depending on the
type of surface of the ground or floor risk of fire of a structure
Measures r p Type of special risk h z
No measures 1 No special risk 1
Low risk of panic (e.g. structures limited to two
One of the following measures: fire extinguishers, floors with up to 100 persons) 2
fixed manually operated fire extinguishing instal-
lations, manual alarm installations, hydrants, fire 0.5 Average level of panic (e.g. structures for cultural 5
compartments, escape routes and sport events with 100 to 1000 visitors)
Difficulty of evacuation (e.g. structures with
One of the following measures: fixed automati- immobile persons, hospitals) 5
cally operated fire extinguishing installations, 0.2 High risk of panic (e.g. structures for cultural and
automatic alarm installations sport events with more than 1000 visitors) 10
Table 3.2.5.2 Values of the reduction factor r p depending on the Table 3.2.5.4 Values of the factor h z which increases the relative
measures taken to reduce the consequences of fire value of a loss for type of loss L1 (loss of human life)
in case of a special risk
r t Factor reducing the effects of touch and step voltages the total number of persons in the structure (n t ) and between
depending on the type of ground outside the structure the time in hours per year during which persons stay in the
or type of floor inside the structure (Table 3.2.5.1); zone (t z ) and the 8760 hours per year. Thus, there are up to
r p Factor reducing the measures taken to reduce the con- eight loss values:
sequences of fire (Table 3.2.5.2);
r f Factor reducing the risk of fire and explosion of the L = L = r L T n Z t z
t
structure (Table 3.2.5.3); A U n 8760
h z Factor increasing the relative value in case of loss t
of human life (L1) due to the level of panic (Table
3.2.5.4). L = L = r r h Z L F n Z t z
p
f
B V n 8760
Loss of human life (L1) t
Loss must be determined for each risk component relevant to
the structure. Moreover, the structure can be subdivided into L = L = L = L = L n Z t z
O
several zones so that the losses must be assigned to the indi- C M W Z n 8760
vidual zones. t
Thus, the loss value depends on the properties of the zone
which are defined by increase factors (h z ) and reduction fac- where
tors (r t , r p , r f ). In other words, the loss value depends on the L T is the typical mean percentage of victims injured by
relation between the number of persons in the zone (n z ) and electric shock (D1) due to a dangerous event;
www.dehn-international.com LIGHTNING PROTECTION GUIDE 41