Page 54 - 35_DS702_E_2014_Lightning_Protection_Guide
P. 54
The conductance G is calculated from a current and voltage
value or a resistance value R. The conductivity refers to the
conductance G of a material with specific dimensions, e.g.:
I 2
I 3 ¨ Length = 1 m
¨ Cross-section = 1 mm 2
I 1
¨ Material
I 1 = I 2 + I 3 + I 4 + I 5
I 4 The conductance of a conductor can be calculated from these
values without requiring current and voltage values. When po-
sitioning the lightning protection system according to Figure
I 5
3.3.2.1.4, a distinction is made between self-conductance and
mutual conductance.
Figure 3.3.2.1.1 Kirchhoff’s law with nodes ¨ Self-conductance: Conductance of all conductances
connected at one point I (example: Corner of a flat roof:
Self-conductance consists of the sum of the conductances
of the down conductors in the corner and the conductance
node of the two air-termination conductors of the mesh).
I 1
I 5
I 4
I 2
I 3
Figure 3.3.2.1.2 Kirchhoff’s law: Example of a building with a mesh
on the roof
I 11
I 10
I 12
I 1
I 5
I 4
I 2 I
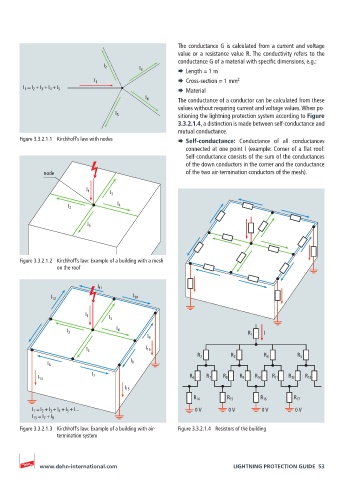
R 1
I 9
I 3 I 16
R 2 R 3 R 4 R 5
I 8
I 6
I 7
I 14 R 6 R 7 R 8 R 9 R 10 R 11 R 12 R 13
I 15
R 14 R 15 R 16 R 17
I 1 = I 2 + I 3 + I 4 + I 5 + I... 0 V 0 V 0 V 0 V
I 15 = I 7 + I 8
Figure 3.3.2.1.3 Kirchhoff’s law: Example of a building with air- Figure 3.3.2.1.4 Resistors of the building
termination system
www.dehn-international.com LIGHTNING PROTECTION GUIDE 53